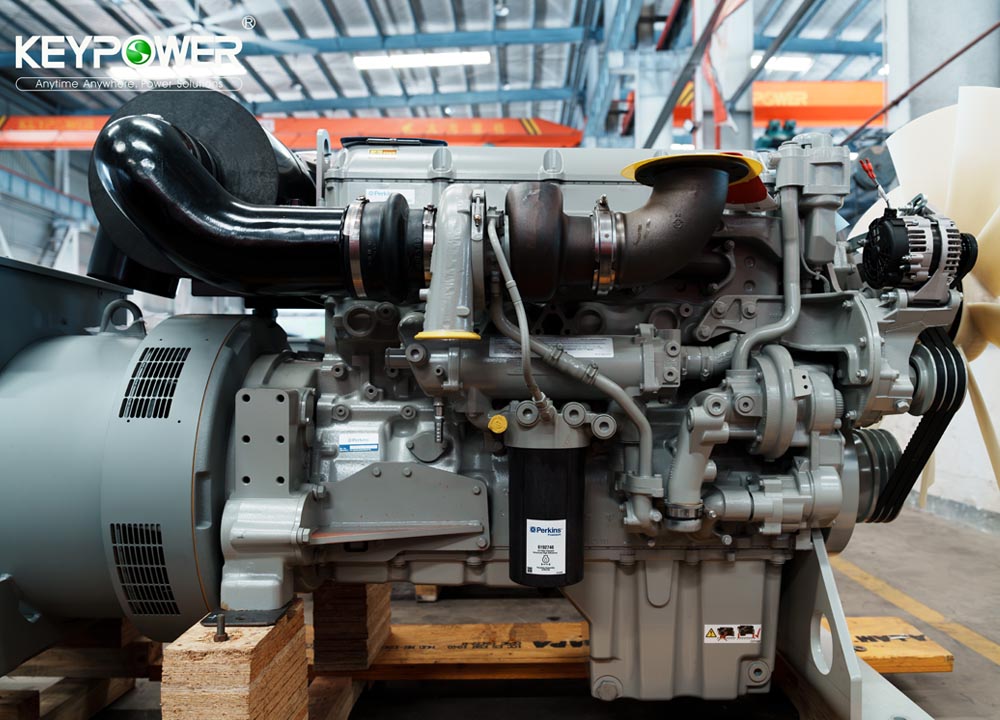
A diesel generator is a machine that converts diesel fuel into electrical energy. It combines a diesel engine with an electric generator (alternator) to produce electricity. These systems are widely used for backup power, prime power in remote areas, or on job sites where grid electricity is unavailable or unreliable.
Key Components:
1. Diesel Engine:
Burns diesel fuel in a compression-ignition cycle (no spark plugs).
High compression ratio (14:1 to 25:1) for efficient fuel combustion.
2. Alternator (Generator Head):
Converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy.
3. Fuel System:
Tank, filters, injectors, and pumps to deliver diesel to the engine.
4. Cooling & Exhaust Systems:
Prevents overheating and vents combustion gases.
5. Control Panel:
Monitors voltage, frequency, and output; starts/stops the generator.
How It Works:
1. Air Intake: Air is drawn into the engine cylinder.
2. Compression: The piston compresses air, heating it to 500–700°C.
3. Fuel Injection: Diesel is sprayed into the hot compressed air, igniting instantly.
4. Power Stroke: Combustion forces the piston down, rotating the crankshaft.
5. Electricity Generation: The spinning crankshaft turns the alternator’s rotor, inducing electrical current in the stator windings.
Why Diesel? Key Advantages:
High Efficiency: 25–40% more fuel-efficient than gasoline generators.
Durability: Robust engines built for heavy loads and long runtimes.
Long Lifespan: Properly maintained units can operate 20,000–30,000+ hours.
Fuel Stability: Diesel stores longer (12–24 months) vs. gasoline (3–6 months).
Torque: Excels at powering high-surge devices (e.g., motors, compressors).
Common Applications:
Backup Power: Hospitals, data centers, factories.
Prime Power: Mining sites, remote telecom towers, off-grid homes.
Emergency Response: Disaster relief, mobile command centers.
Construction: Powering tools at job sites without grid access.
Post time: Jun-19-2025